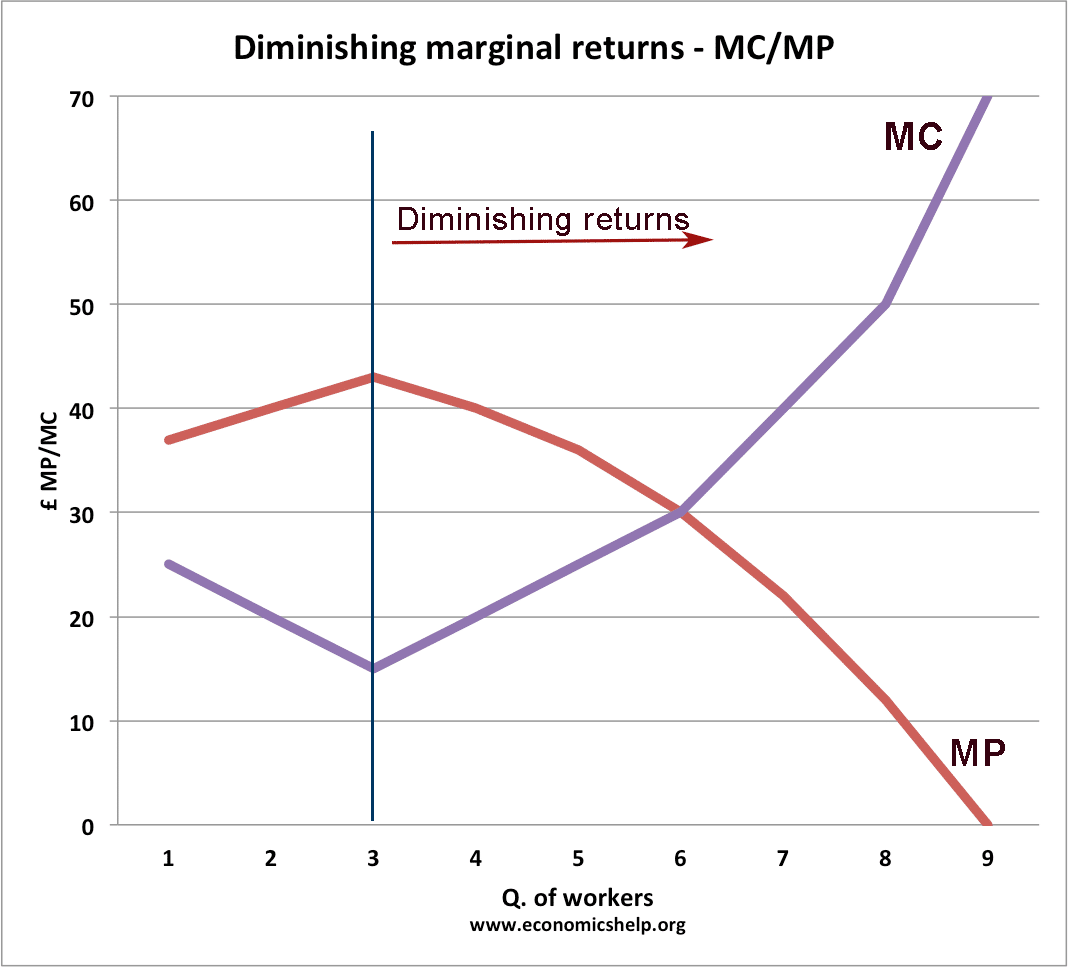
The Law of Diminishing Marginal Returns
Definition: Law of diminishing marginal returns At a certain point, employing an additional factor of production causes a relatively smaller increase in output. Diminishing returns occur in the short run when one factor is fixed (e.g. capital) If the variable factor of production is increased (e.g. labour), there comes a point where it will become …